| Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2017 Mar; 10(3): 297–309. |
| Salvage therapy using self-expandable metal stents for recalcitrant anastomotic strictures after living-donor liver transplantation |
| Consequently, the aim of this study was to examine the feasibility and efficacy of using a newly designed fully covered self-expandable metal stent (FCSEMS) to resolve refractory ABS. A total of 35 FCSEMSs were positioned endoscopically and removed after 2-3 months. The anastomotic stricture resolved with the FCSEMS insertion in 29 of 35 patients (clinical success rate: 82.9%). The newly designed FCSEMS: KAFFES™ Stent is a potentially feasible and effective treatment for anastomotic strictures that develop after LT but are not amenable to treatment by conventional procedures. |
|
|
|
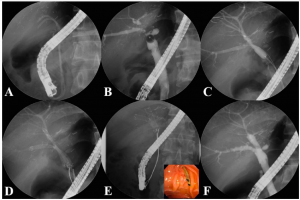
Insertion procedure for multiple FCSEMSs. (A) Previously inserted plastic stents are removed endoscopically. (B) The cholangiogram shows multiple anastomotic strictures at the posterior and inferior intrahepatic ducts. (C) The strictures are dilated using a balloon dilator to allow passage of the FCSEMSs. (D) The FCSEMSs are inserted sequentially into the stricture sites. (E) After an indwelling time of 2–3 months, the FCSEMSs are removed by grasping the retrieval strings using biopsy forceps. (F) The cholangiogram demonstrates resolution of the multiple strictures. |